Beginners' Guide to Effortless Doctests in Python
Doctests are essentially tests embedded in a docstring. They serve both as example use cases and test cases! A Python expression is provided along with an expected outcome, a test runner collects that and evaluates the expression.
Getting started
Let's take a look at a run-of-the-mill docstring.
def hello(name):
"""
Returns a greeting message saying Hello.
:param name: str
:return: str
"""
return 'Hello, ' + name
It's a normal docstring with nothing too special. Let's try to get the doctest module to test our test-less function.
$ python -m doctest -v hello.py
2 items had no tests:
hello
hello.hello
0 tests in 2 items.
0 passed and 0 failed.
Test passed.
Well, the output says it clear that we have no tests. Now, let's add a doctest. Remember how the Python Shell or REPL works? Remember how you have three arrows indicating input? Yes. Just copy that style.
def hello(name):
"""
Returns a greeting message saying Hello.
:param name: str
:return: str
>>> hello('Anam')
'Hello, Anam'
"""
return 'Hello, ' + name
Time to run the doctest module again.
$ python -m doctest -v hello.py
Trying:
hello('Anam')
Expecting:
'Hello, Anam'
ok
1 items had no tests:
hello
1 items passed all tests:
1 tests in hello.hello
1 tests in 2 items.
1 passed and 0 failed.
Test passed.
Ah, that looks more like it.
Expecting Exceptions
Let's try something more fun. Let's add a case in our function, if the provided name is just composed of digits, we refuse to greet digits!
def hello(name):
"""
Returns a greeting message saying Hello.
:param name: str
:return: str
>>> hello('Anam')
'Hello, Anam'
"""
if name.isdigit():
raise ValueError('We do not greet numbers')
return 'Hello, ' + name
Now, how do we test for exceptions? Well, remember the mantra.
Replicate your shell; success you will be showered with upon you.
So, just replicate your shell! Let's see how the shell reacts to digits.
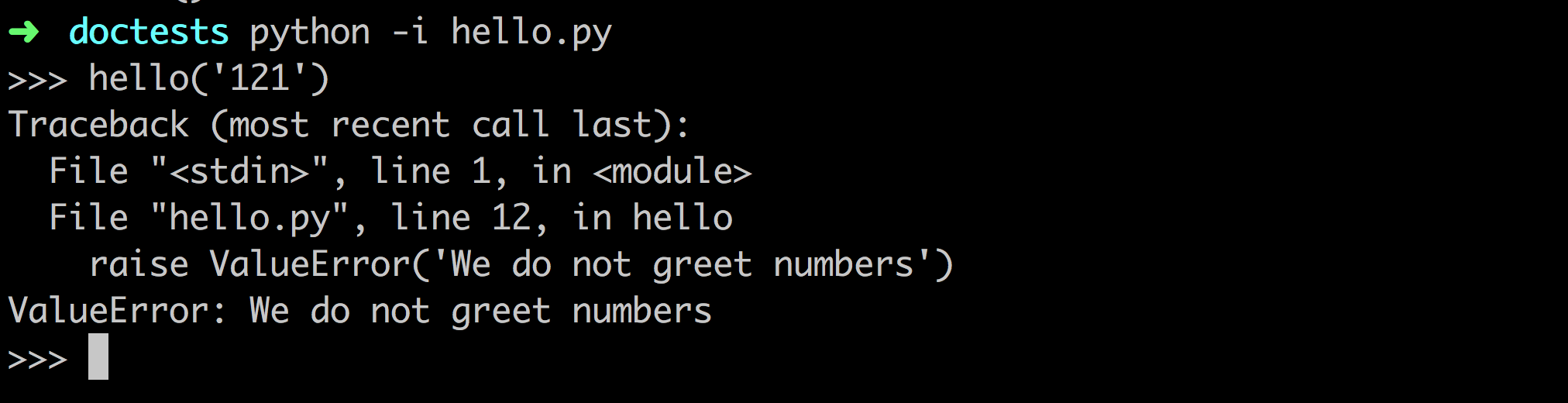
So, in the doctest,
def hello(name):
"""
Returns a greeting message saying Hello.
:param name: str
:return: str
>>> hello('Anam')
'Hello, Anam'
>>> hello('121')
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
ValueError: We do not greet numbers
"""
if name.isdigit():
raise ValueError('We do not greet numbers')
return 'Hello, ' + name
Just the first line and the last line of the exception. Don't confuse doctest with a complete, well-formatted and fully laid out stack trace, please! And just three dots to indicate there were more to it. So, let's run this again.
$ python -m doctest -v hello.py
Trying:
hello('Anam')
Expecting:
'Hello, Anam'
ok
Trying:
hello('121')
Expecting:
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
ValueError: We do not greet numbers
ok
1 items had no tests:
hello
1 items passed all tests:
2 tests in hello.hello
2 tests in 2 items.
2 passed and 0 failed.
Test passed.
And yes.
In Production
Of course, in production, you do need to use a test runner. Something in the category of pytest or nose. I personally prefer pytest. Let's take a look at configuring pytest for this.
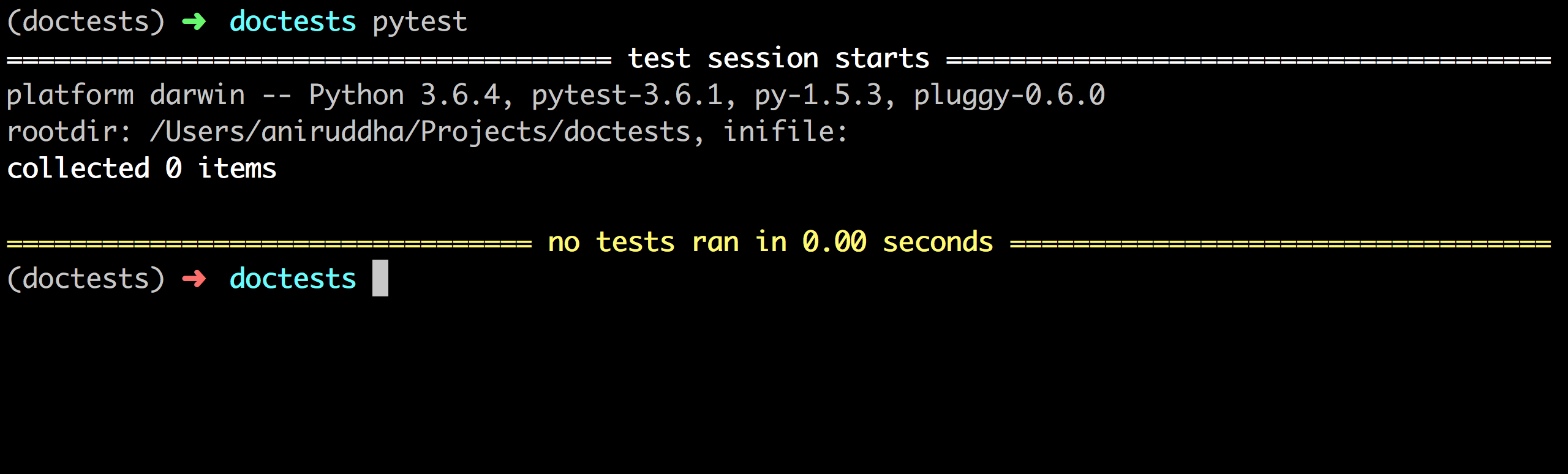
Not so surprisingly, it discovered no tests in the default configuration. We need to add a simple flag to it --doctest-modules .
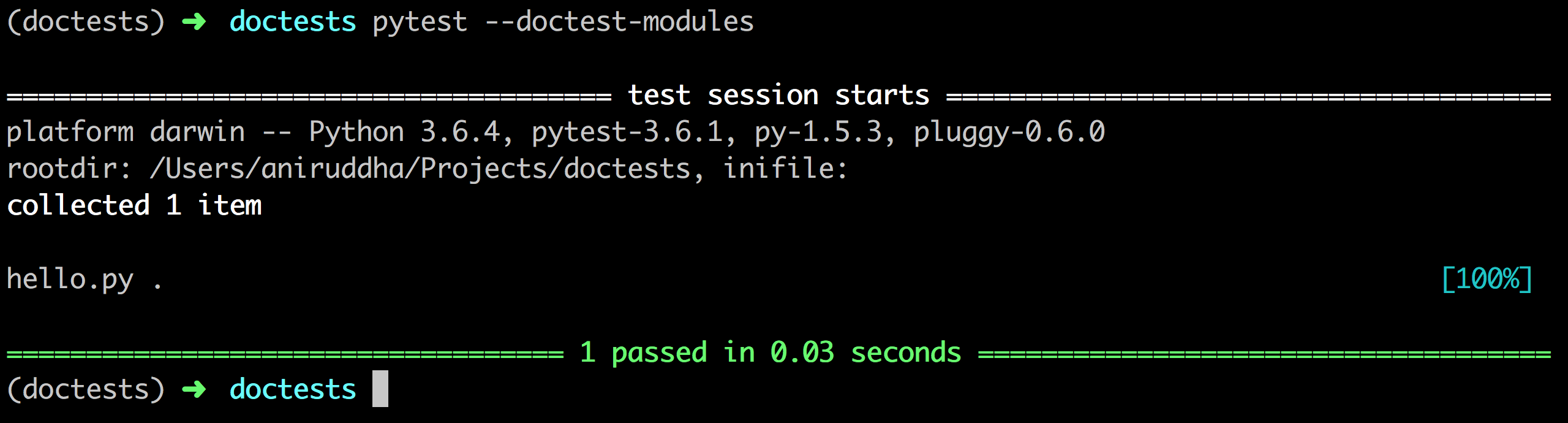
That seems to be working, let's try to intentionally run our tests to check if it is really working.
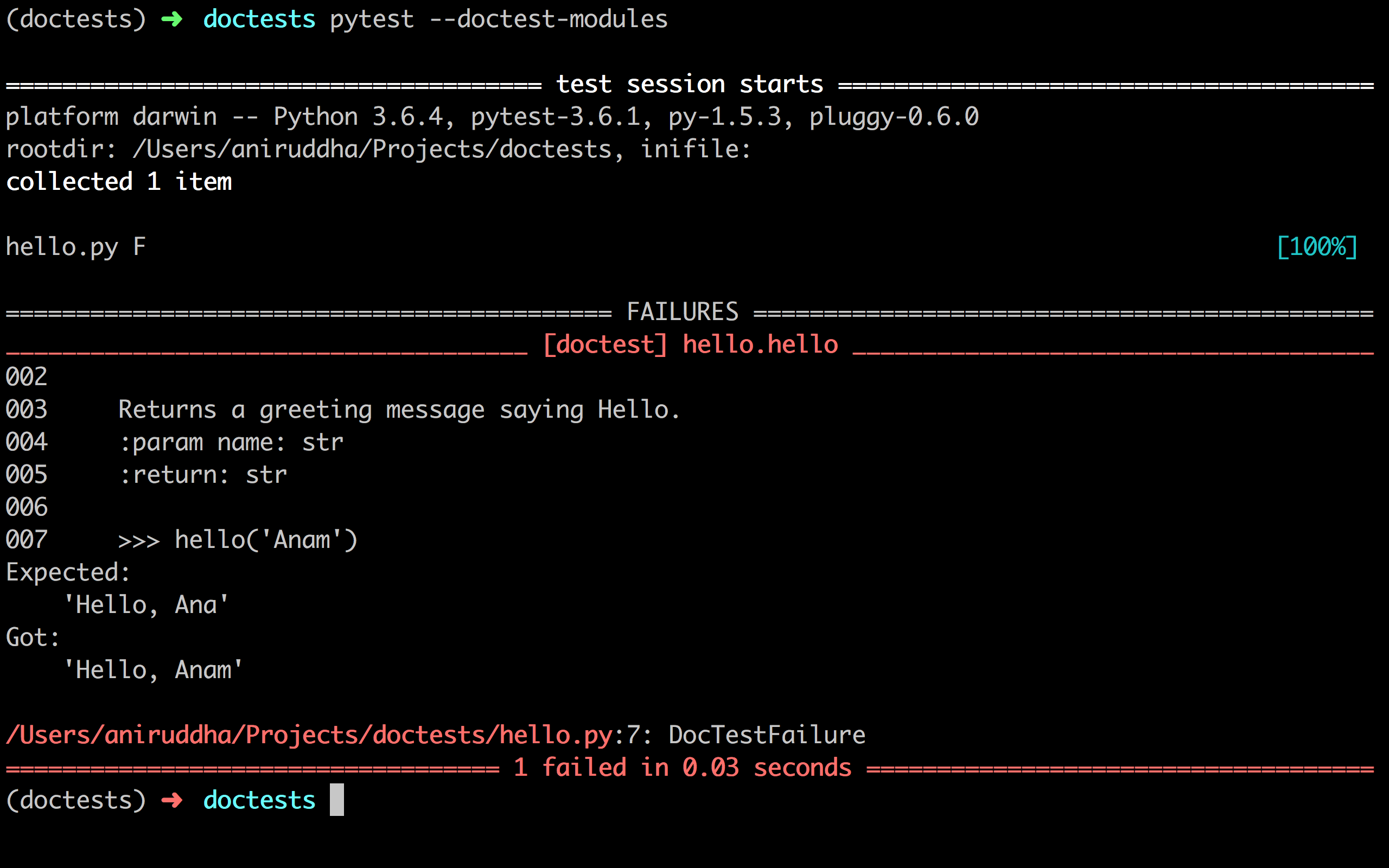
And that is working perfectly. To avoid putting the --doctest-modules flag all the time, consider making a tox.ini file to place your pytest configuration. More on this in the pytest documentation.